ADDICTION
ALCOHOL DEPENDENCE
QUIT SMOKING
ALLERGY
ANTI FUNGAL
FUNGAL INFECTION
FUNGAL NAIL INFECTIONS
ANTI-REJECTION DRUGS
ANTI WORM
ANTIBIOTIC
BACTERIAL INFECTIONS
ARTHRITIS
GOUT
OSTEOARTHRITIS
RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS
BLOOD
LOW PLATELET COUNT
THROMBOPHLEBITIS
VARICOSE VEINS
COLON
ANAL FISSURE
PILES
ULCERATIVE COLITIS
DIABETES CARE
DIABETES INSIPIDUS
DIABETES TYPE
DIABETIC FOOT ULCERS
GLUCOSE MONITOR
EYES/EAR CARE
DRY EYES
EYE CARE
EYE EXAMINATION
EYE INFECTION
EYE LASHES
EYE PAIN
GLAUCOMA
OCULAR HYPERTENSION
UVEITIS
FEVER CARE
MALARIA
RHEUMATIC FEVER
TYPHOID FEVER
GASTROINTESTINAL
ACIDITY
CONSTIPATION
CROHN'S DISEASE
DIARRHOEA
GALLBLADDER STONES
INTESTINAL ULCERS
IRRITABLE BOWEL SYNDROME
MOTION SICKNESS
NAUSEA
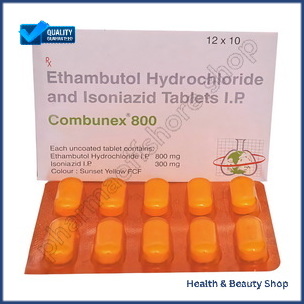
Combunex 800 mg (Ethambutol/Isoniazid)
| Active Ingredient (Generic Name): | Ethambutol/Isoniazid |
|---|---|
| Indication: | Tuberculosis (TB) |
| Manufacturer: | Lupin Limited |
| Packaging: | 10 tablets in one strip |
| Strength: | 800 mg |
From: $26.00
Combunex 800 mg, a combination of Ethambutol and Isoniazid, is prescribed to treat tuberculosis and mycobacterial infections. This medication works by targeting different aspects of bacterial cell wall synthesis to enhance antibacterial effects. It is essential to complete the full treatment course for optimal effectiveness. Monitor your vision and liver function during treatment, and be aware of potential gastrointestinal and central nervous system reactions. Follow the dosage guidelines and precautions to ensure effective treatment. Be aware of potential interactions with other medications.
Main Points
? Combunex 800 mg is a medication composed of 800 mg of Ethambutol and Isoniazid, used to treat tuberculosis and mycobacterial infections.
? The combination of Ethambutol and Isoniazid enhances antibacterial effects by inhibiting arabinogalactan and mycolic acid synthesis, respectively.
? The dual-action mechanism targets TB bacteria, disrupting bacterial cell wall synthesis. Adherence to the treatment course is crucial for effectiveness.
? The typical adult dosage is 15-25 mg/kg daily. Completing the full treatment course is essential to prevent drug-resistant TB strains.
? Common side effects include gastrointestinal reactions, CNS reactions, and interactions with other medications. Careful monitoring is required.
What Is Combunex 800 mg?
Combunex 800 mg is a fixed-dose combination medication containing 800 mg of Ethambutol and Isoniazid. These antibacterial agents are prescribed to treat tuberculosis and other mycobacterial infections.
Ethambutol inhibits the synthesis of arabinogalactan, a component of mycobacterial cell walls. Isoniazid inhibits the synthesis of mycolic acid, a component of mycobacterial cell membranes. The combination of these two agents enhances their antibacterial effects.
Combunex 800 mg is prescribed as part of a treatment regimen for tuberculosis and other mycobacterial infections. To ensure effective treatment, patients should follow their healthcare provider’s instructions and complete the full treatment course.
How Combunex 800 mg Works
Combunex 800 mg is a combination of two antibiotics: Ethambutol and Isoniazid. These antibiotics target different aspects of tuberculosis (TB) bacteria. Ethambutol inhibits the formation of the mycobacterial cell wall. Isoniazid interferes with the synthesis of mycolic acids, essential for bacterial growth. The combination of these mechanisms makes Combunex 800 mg effective in treating TB.
Mechanism of Action
Combunex 800 mg is used to combat tuberculosis. The medication contains two active ingredients: ethambutol and isoniazid. These ingredients disrupt the synthesis of mycolic acids, which are essential components of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis cell wall.
Ethambutol inhibits arabinosyltransferase, an enzyme necessary for mycolic acid synthesis. This inhibition prevents the formation of new cell walls, leading to the death of bacterial cells. Isoniazid inhibits enoyl-acyl carrier protein reductase, another enzyme involved in mycolic acid synthesis. This inhibition contributes to the bactericidal effects of Combunex 800 mg.
Combunex 800 mg Effects
Combunex 800 mg’s dual-action mechanism, comprising ethambutol and isoniazid, disrupts Mycobacterium tuberculosis growth by targeting the bacterial cell wall. Ethambutol inhibits arabinogalactan production, a key cell wall component, while isoniazid interferes with mycolic acid synthesis, a vital fatty acid in the cell wall. This dual disruption weakens the bacterial cell wall, ultimately leading to cell death.
Consistent Combunex 800 mg treatment reduces Mycobacterium tuberculosis growth rates, resulting in bacterial cell death and effective tuberculosis treatment. Adhering to the prescribed treatment regimen, as directed by a healthcare provider, is crucial for optimal treatment outcomes. Understanding Combunex 800 mg’s mechanism of action highlights the importance of consistent treatment adherence.
Uses of Ethambutol and Isoniazid
Ethambutol and Isoniazid are used to treat tuberculosis (TB). These medications are often combined to combat the disease. They help prevent resistance and manage TB infections. Ethambutol and Isoniazid are used to treat active TB and prevent latent TB infections.
Tuberculosis Treatment Options
Combunex 800 mg, a fixed-dose combination of ethambutol and isoniazid, is a key component in tuberculosis treatment, particularly during the initial intensive phase. This medication is typically taken in conjunction with other drugs as part of a multi-drug regimen to prevent the development of drug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis strains.
Throughout treatment, healthcare providers closely monitor patient progress, adjusting dosages or medication regimens as necessary. In addition to Combunex 800 mg, treatment plans may include antibiotics such as rifampicin, pyrazinamide, or streptomycin. The specific regimen depends on the severity of the tuberculosis, patient age, and any underlying health conditions.
Adherence to the prescribed regimen is crucial, even if symptoms improve before completing the full course of therapy. Non-adherence can lead to treatment failure, relapse, or the development of drug-resistant tuberculosis. By following the treatment plan, patients can effectively manage their tuberculosis and increase the likelihood of a successful outcome.
Prevention of Resistance
To prevent the emergence of resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis strains, ethambutol and isoniazid play crucial roles in inhibiting bacterial growth, reducing the likelihood of resistance development during tuberculosis treatment. These medications work synergistically to suppress Mycobacterium tuberculosis growth, making it more challenging for the bacteria to develop resistance.
When taken together, ethambutol and isoniazid create an environment that hinders bacterial mutation and adaptation. Ethambutol inhibits arabinogalactan production, an essential component of the mycobacterial cell wall, while isoniazid disrupts mycolic acid synthesis, essential for bacterial growth. By targeting different stages of bacterial growth, the likelihood of resistance development is reduced.
TB Infection Management
Treating active tuberculosis infections often involves combining ethambutol and isoniazid. This combination helps combat Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the primary cause of TB. Ethambutol and isoniazid work together to inhibit mycolic acid synthesis, which is essential for the mycobacterial cell wall. By disrupting this process, the combination therapy restricts TB bacterial growth, allowing the immune system to gain control over the infection.
Combunex 800 mg, which contains ethambutol and isoniazid, reduces the severity of symptoms such as coughing, fever, and fatigue. Adhering to the treatment regimen as directed is essential to prevent the development of drug-resistant TB strains. The combination of ethambutol and isoniazid is crucial for overcoming TB and regaining health.
Combunex 800 mg Dosage Guidelines
Combunex 800 mg Dosage Guidelines
The dosage of Combunex 800 mg is determined by a doctor based on body weight and the severity of the tuberculosis infection. The typical adult dosage is 15-25 mg/kg of body weight daily, divided into 2-3 doses. The dosage may be adjusted based on individual needs.
The following table provides general guidelines for Combunex 800 mg dosages based on body weight:
| Body Weight (kg) | Daily Dosage (mg) |
|---|---|
| 30-39 | 750-1000 |
| 40-54 | 1000-1300 |
| 55 and above | 1300-1600 |
Take Combunex 800 mg exactly as directed by a doctor. Do not skip doses or stop taking the medication without consulting a doctor, as this can lead to treatment failure or relapse. Complete the full treatment course, typically 6-9 months, to ensure effective treatment of the tuberculosis infection.
Side Effects to Watch For
When taking Combunex 800 mg, be aware of potential side effects. Gastrointestinal reactions, including nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain, are common. Central Nervous System reactions, such as headaches, dizziness, and fatigue, may occur.
Gastrointestinal Reactions
Gastrointestinal Reactions
Combunex 800 mg may cause gastrointestinal reactions, including nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. These symptoms can range from mild to severe and may require medical attention if they persist or worsen over time.
Report any changes in your digestive health to your doctor, as they may need to adjust your dosage or recommend additional medications to alleviate these side effects.
In some cases, gastrointestinal reactions can lead to more severe complications, such as gastrointestinal ulcers or bleeding. If you experience severe abdominal pain, vomiting blood, or black tarry stools, seek immediate medical attention.
Your doctor may recommend antacids or other medications to manage your symptoms. Maintaining a healthy diet, staying hydrated, and avoiding triggers that may exacerbate your gastrointestinal reactions are also crucial.
Central Nervous System
Combunex 800 mg can cause central nervous system side effects, including headache, dizziness, and fatigue. These effects may impact daily activities and require prompt medical attention if severe or persistent.
Numbness or tingling sensations in the hands and feet, known as peripheral neuropathy, may occur. This can be a sign of nerve damage. In rare cases, seizures may develop, particularly in individuals with a history of seizure disorders.
Combunex 800 mg can also affect mental health, causing changes in mood, anxiety, and depression. Lethargy, apathy, or withdrawal may occur, which can impact relationships and daily life. If unusual changes in thoughts, feelings, or behavior are noticed, consult a doctor.
Interactions With Other Medications
Interactions With Other Medications
Medications that induce liver enzymes, such as rifampicin, may accelerate the metabolism of isoniazid, potentially reducing its therapeutic effect.
| Medication | Interaction || Rifampicin | Induces liver enzymes, reducing isoniazid’s effect || Carbamazepine | Increases risk of hepatotoxicity when combined with isoniazid || Phenytoin | Enhances metabolism of isoniazid, reducing its effect || Theophylline | Increases risk of theophylline toxicity when combined with isoniazid || Cycloserine | Increases risk of neurological side effects when combined with isoniazid |
When taking Combunex 800 mg, inform your doctor about all medications you’re currently taking, including prescription and over-the-counter drugs, vitamins, and supplements. This helps avoid potential interactions and promotes the safe and effective use of Combunex 800 mg.
Precautions and Contraindications
To minimize the risk of adverse effects and maximize therapeutic benefits when using Combunex 800 mg, take the following precautions:
- Monitor your vision, as Combunex 800 mg can cause optic neuritis. Report any changes in vision to your doctor immediately.
- Regular blood tests may be ordered by your doctor to monitor liver function and detect potential liver damage.
- Be aware of signs of peripheral neuropathy, such as numbness, tingling, or pain in your hands and feet. Consult your doctor if you experience any of these symptoms.
Contraindications for Combunex 800 mg include:
- Severe kidney or liver disease
- Optic neuritis
- History of hypersensitivity to ethambutol or isoniazid
Combunex 800 mg and Pregnancy
Combunex 800 mg and Pregnancy: Weighing Risks and Benefits
When pregnant or planning to become pregnant, discuss Combunex 800 mg‘s potential risks and benefits with your doctor. This medication, containing ethambutol and isoniazid, is categorized as pregnancy category C, indicating potential adverse effects on the fetus. However, in certain situations, the benefits of taking Combunex 800 mg may outweigh the risks, particularly for active tuberculosis.
Inform your doctor about your pregnancy or plans to become pregnant, and they will assess your individual situation and make an informed decision. If taking Combunex 800 mg during pregnancy, your doctor will closely monitor you and your fetus for potential complications. Adhere to the prescribed dosage and duration to minimize risks. Regular prenatal check-ups are essential to ensure the health and well-being of both you and your fetus. It is crucial to weigh Combunex 800 mg’s benefits against potential risks to make an informed decision about your treatment.
Overdose Symptoms and Treatment
Accidental or intentional overdose of Combunex 800 mg can occur. Recognizing the symptoms and seeking immediate medical attention are crucial.
Overdose symptoms include:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Dizziness and confusion
- Seizures and convulsions
- Respiratory depression
If an overdose is suspected, call a doctor or emergency services. Treatment typically involves supportive care, including administering activated charcoal to absorb the drug and providing oxygen therapy to manage respiratory depression. In severe cases, hospitalization may be necessary to monitor and treat complications.
Storing and Disposing Combunex 800 mg
Store Combunex 800 mg in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight and moisture, to maintain its potency and shelf life. Keep the tablets in their original packaging or a tightly closed container to protect them from air, light, and humidity. Store Combunex 800 mg out of reach of children and pets to avoid accidental ingestion.
Dispose of unused or expired Combunex 800 mg tablets through a pharmacy or designated drug take-back program. Do not flush them down the toilet or throw them away in household trash. Proper disposal helps prevent environmental pollution and minimizes the risk of medication misuse. Consult your pharmacist or healthcare provider for specific guidance on storing and disposing of Combunex 800 mg.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I Crush or Split Combunex 800 mg Tablets?
Crushing or splitting Combunex 800 mg tablets is generally not recommended. This alteration can disrupt the drug’s intended release mechanism, potentially affecting its efficacy.
Is Combunex 800 mg Effective Against Viral Infections?
Combunex 800 mg is ineffective against viral infections. As an antibacterial medication, it is specifically designed to combat tuberculosis, not viral infections, and therefore will not provide relief.
Can I Take Combunex 800 mg With Antacids or Dairy Products?
Taking Combunex 800 mg with antacids or dairy products is not recommended. This combination can reduce the absorption of isoniazid, a key component, which may decrease its effectiveness in treating bacterial infections.
Does Combunex 800 mg Affect DNA or Cause Genetic Mutations?
Isoniazid, a component of Combunex 800 mg, does not directly affect DNA or cause genetic mutations. However, it can inhibit DNA synthesis and repair, potentially leading to indirect genetic effects.
Can Combunex 800 mg Be Used to Treat Latent Tuberculosis?
Combunex 800 mg is a fixed-dose combination of antibacterial agents effective against Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It is a suitable treatment option for latent TB infection.
Conclusion
Combunex 800 mg is a medication that combines ethambutol and isoniazid to treat tuberculosis. It works by preventing the growth of tuberculosis-causing bacteria. The recommended dosage is as directed by a doctor. Common side effects include vision problems, joint pain, and nausea. In rare cases, it can cause liver damage or allergic reactions. Store Combunex 800 mg in a cool, dry place. In case of overdose, seek immediate medical attention. Follow the prescribed regimen and monitor your body’s response. Report any concerns to your doctor.




There are no reviews yet.